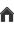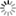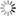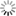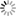Saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers
The Venice case study.
In the right images:
a) map of the depth of the saltwater contamination plume. The areas belonging to the first class (0-5 m) are most at risk of desertification as the saltwater contamination directly involves the plant and crop root zone.
b) depth of the bottom of the saltwater contamination plume.
c) vertical cross sections obtained from airborne electromagnetics (SkyTEM) survey. The salt water plume flows from the lagoon into the coastal aquifer system.
The saltwater contamination plume extends up to 20 km inshore and is enhanced by land elevation, generally below the mean sea level, the geomorphological structures (i.e., sandy paleo-channels crossing the farmland with main direction from inland to the lagoon of the coastal plain), and the seawater encroachment along the hanging last portion of the watercourses.